Parents need to pay much attention to the physical development of their children in order to correct the shortcomings over time.Valgus deformation of the foot in children is a common pathology.Although the defect is congenital or acquired, the methods of diagnosis, prevention and correction are similar.
What is valgus and leg with flat valgus
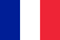
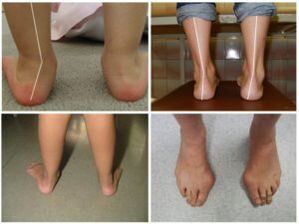
The term valgus doctors mean any curvature of the joints inside of the conditional middle line (axis), in which a marked "X-shaped" deviation is observed.The most pronounced example of pathology is the bones of the thumbs (Hallux valgus).Valgus deformation, which is shortened as a "valgus foot" (sun), is the wrong setting of the foot of the horizontal support.If the baby -a year old baby assembles the legs, then the back is noticeable as the inner ankle moves closer to the opposite limb and the heel deviates from the outside.At the same time, a flat child relies mainly on the internal (medial) part of the foot.Therefore, the plantar region, as it was, "looks."A variety of disease is a flat valgus foot (PVS).It combines flat legs with a curvature of X-shape.In the baby, in addition to the formation of deformation, the set of the foot is gradually leveled.
Valgus curvature
The stage of neglect of the pathology is determined by the size of the angle of deviation of the heel of the middle axis.
There are 4 degrees of disease:
- I - up to 15 °;
- II - 15tes;
- III - 20® °;
- IV - 30 ° or more.
Stage 1-2 Deformation of Valgus can be eliminated by conservative methods.Prolonged treatment is required by 3 degrees.Surgical correction may be required at 4 stages.
The reasons for deformation
There are three factors that cause the foot curvature: impaired intrauterine development, chronic physical overload, diseases of the musculoskeletal system.These factors weaken the connections, tendons, muscles so that the leg is not fixed by them in a normal anatomical position.
The reasons for the acquired valgus, a flat volgus foot (code M21.0 in ICD-10):
- Premature leg adjustment when the baby's joints are not yet ready for such loads;
- "Wrong" shoes (a narrow block with a thin high heel, no souinators).
- muscular hypotension, congenital myodystrophy;
- Great weight, obesity;
- rickets;
- neuromuscular diseases (polio, pediatric cerebral palsy, polyneuropathy of different etiologies);
- congenital dislocation of the thigh and dysplasia of the hip joints;
- trauma to the foot or lower legs;
- Long -term immobilization of the legs with gypsum, teacher or pillow of Frake.
The congenital origin of the valgus defect and a flat valgus of the foot structure (Q66.6 code in ICD-10) may be due to injury to the abdomen transferred from a pregnant woman or a genetic disease.Such curvature can be seen immediately after birth, sometimes it manifests itself before the baby starts walking.
How to determine the deformation of a stop
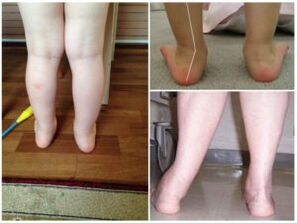
The change in the lower limb configuration is placed along the axis of the leg.This is the name of the conventional line, visually drawn from the center of the hip joint through the knee, the ankle to the middle of the calcaneus.The norm implies the passage of the axis through the center of the joints, which should not be displaced from it to the right or left.
Characteristics
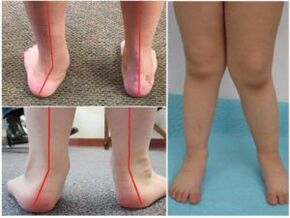
In newborn babies, with the congenital nature of Valgus, it occurs immediately or during the first months of life.Most often, signs of Valgus defect in children appear in a year and a half.The presence of the disease can be suspected of the baby's behavior and gait.The following common symptoms of pathology are most commonly detected:
- increased flexibility of small joints;
- Reducing the height of the set of the sole;
- The displacement of the center of gravity (when trying to walk, the child relies only on the medial side of the foot, his outer edge can slightly rise);
- uncertain, stirring gait;
- Rapid physical fatigue, the need for rest, to let the baby relax;
- Regular complaints of leg pain, unwillingness to walk;
- light swelling and redness of the skin in the foot and ankle;
- Uneven wear of shoes, more pronounced than the inner edge of the sole.
Methodology for identifying deformation
Defect diagnostics methods include examination with the baby's leg orthopedics, followed by the baby's direction for instrumental examination.It is made x -ray on the feet in three projections to find the degree of bone displacement.They also perform planeography to determine the height of the planet and the severity of the flat legs.Using a post -meter, the pressure center on the sole is calculated.This is an effective diagnostic method as it allows you to identify valgus deformations in the early stages.Sometimes, to clarify the results of the study, an ultrasound of the foot is made.The visual signs of pathology are the only one slightly inverted and lifted in a side direction, displacement of the heel, out from the midline.Deformation of flat valgus is noted the disappearance of the vault, the leveling of the foot.In order to rule out the neurological causes of the defect, the orthopedist directs the child to a narrow specialist.
Adjustment methods
In order to eliminate valgus, the main tasks are to give the foot of the correct position and the subsequent strengthening of the connections attached to the tendons of the heel and muscles.
Fixing the joint in a conservative manner
Plaster bandages or teachers are used with a congenital defect.The purpose of the firm fixation of the foot under the right corner is to eliminate the curvature by immobilization.While the ossification is not completed, the tissues are elastic, so they are easily subject to such a correction.With the acquired defect of Valgus, to restore the proper adjustment of the foot, the child is made orthopedic shoes.It should not cause discomfort when used.A special shoe insole has side hard supercers, a soft pillow (pelot) under the vault of the foot.Such shoes are also recommended to wear during rehabilitation after surgery and to consolidate the results of the treatment.
A variety of insoles with valgus foot
Experts recommend ordering orthoses, shoes or insoles for children in orthopedic salons according to separate sizes and castings of the foot.The price of the product will be a little higher, but the use will give a more noticeable result.
Strengthening of small joints
For the general hardening and tonic muscles of the lower limbs, it is recommended to use contrasting foot baths.For this, the legs are immersed sequentially in a container of cold and warm water.They start with a temperature of 36 ° C with fluid, after which this value changes every week by 1 ° C gradually, reaching a range of 14 to 40 ° C
It is useful to do the following exercises:
- Alternative walking on socks, heels, interior, outer edges of the sole;
- collecting small objects, squeezing tissue or paper, painting with toes;
- The sking ball sole on the floor;
- a set of finger exercises (bending-strain, reproduction and closure);
- Walking on pebbles and an uneven surface.
The orthopedist may prescribe a massage course of the lumbar spine affected by the lower limb or both legs.It is optimal to do so after heating with paraffin or ozoket administration.The muscles of the inner surface of the legs are acting by movement of tonic massage (tapping, mixing).The outer surface of the legs should be massaged with relaxing techniques - breeze, rubbing.
Physiotherapy procedures
If the deformity of the foot causes inflammation of the joint structures, the tendons of the muscles, the child is prescribed electrophoresis with painkillers and anti -inflammatory drugs, magnetotherapy, administration of black wax, paraffin and therapeutic mud.Diadeamic currents are used for selective muscle stimulation.
Surgical treatment
In early childhood, radical methods of therapy are not used.But if the defect interferes with normal walking, the surgery is performed on young children.During surgery, doctors using metal elements (titanium wire, screws, slabs) fix the deformed joint in the normal position.Surgeons can also enhance the joint by moving the tendon of the fibula or lengthening the Achilles tendon.After these operations, rehabilitation involves the use of orthopedic products, massage, physiotherapy and physiotherapy exercises.
Preventive measures
To prevent the deformation of valgus on the foot, you need to buy comfortable shoes that match the size of the leg, the anatomical structure of the foot.How to choose - Watch E.o.'s recommendations.Komarovsky on the video.The doctor says of the disease that this is a common disorder in children and helps to properly form the foot by the age of 12.The teenager most likely needs surgery to correct the pronounced defect of the foot.The child should walk barefoot on sand, grass, walk a lot, eat completely.Dosage sunbathing prevents kicks in children, which is one of the causes of the disease.Physical upbringing, hardening of the body, regular courses for general strengthening massage.Gymnastics for the muscles of the foot is also important, including creating a model of foot in the sand.Active outdoor games, swimming also contributes to the strengthening of the muscles and connections of the lower limbs.All these measures prevent the development of leg defects.It is forbidden to put the child's feet up to 7.5 GRA P.8 months, when the joints and bones of the lower limbs have not yet been strengthened.It is unacceptable to miss the planned pediatrician exams and narrow specialists who allow you to identify the pathology at an early stage.
Doctors 'answers to parents' questions
How do I warn Valgus's congenital deformation?Unfortunately, a defect in the development of the musculoskeletal system cannot be prevented.Even if they have not found abnormalities in the hospital, the baby should be regularly inspected by a pediatrician, receive a massage, walk barefoot on an uneven but safe foot surface.It is recommended to use a massage carpet at home.The acquisition of high quality shoes also helps to put the foot in the right position to form a set of physiological heights.Such prevention will stop the progression of Valgus's uniform leg.
Which doctor treats the pathology?
If necessary, the pediatrician directs the baby to the baby orthopedist, traumatologist, surgeon.
What is a variant leg?
The variants are the displacement of the bone of the heel inside the midline.In this case, the set of the foot is made very high and the pressure center is shifted to the outer edge of the sole.The defect is treated with the same methods as the deformation of Valgus, only the angle of deviation is regulated on the opposite side of the foot.
Valgus deformation of the foot in children: consequences and correction
Valgus deformation of the foot is a pathological change in the musculoskeletal system, in which the height of the set of the foot decreases and the axis of the lower limbs shifts.
The defect can be congenital or develop in childhood, leading to flat feet, disruption of posture and other health problems.As a rule, it is corrected conservatively, in the course of long therapy with charging, massages, physiotherapy.With regular deformation work, you can achieve the right leg adjustment and a confident gait.
Foot Deformation with Flat Valgus in Children-Symptoms
This leg defect can be recognized by the following external signs:
- The leg is strewn with the inner rib, the child rests on the inside of the foot;
- The heel and fingers are located outside;
- The middle part of the foot is flat or noticeably reduced;
- When the knees are reduced, the legs take the shape of the IX, the legs do not approach together, between them there is a distance of about 4-5 cm;
- Uncertain, clumsy gait, the child is often stabbed, stirred;
- The kid quickly gets tired of walking.
When can a defect occur?
The arch of the foot begins to form from the moment the baby is trying to take the first steps.Babies are considered a flat leg for the norm.When they occupy a vertical position independently, children develop a musculoskeletal system, "accustomed" to new functions.Bones and connections begin to experience loads, the leg is strengthened and takes the right anatomical shape.This usually happens up to 1.5 years.If by this age the vaults remain flat, there is no form, doctors define this as a deformation of valgus on the foot.As a rule, violations are detected in medical examinations, but if parents independently notice the above characters, you should contact an orthopedist immediately.If you start adjusting as early as possible, recovery is faster and without serious consequences.
Conclusion
Parents should spend the maximum time preventing the baby's physical development, including gymnastics, massage courses and other entertainment activities.If the deformation of the valgus of the foot in children is not eliminated by conservative treatment, then you must agree to surgery to correct the shape of the foot.In the end, advanced pathology is fraught with the development of arthrosis, spinal diseases and shortening of the limb.